m Fixed incorrect labeling of PBS_Metallic as a Metallic-Roughness shader when it is in fact a Metallic Smoothness shader |
989onan bot (talk | contribs) Automated: update 'StencilComparison' description,'StencilOperation' description,'StencilID' description,'StencilWriteMask' description,'StencilReadMask' description,'RenderQueue' description,'BlendMode' description,'Sidedness' description,'ZWrite' description,'ZTest' description,'OffsetFactor' description,'OffsetUnits' description, |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
== Usage == <!--T:3--> | == Usage == <!--T:3--> | ||
{{Table ComponentFields | {{Table ComponentFields | ||
|HighPriorityIntegration|Bool| | |HighPriorityIntegration|Bool|{{Asset HighPriorityIntegration Field}} | ||
|_shader|Shader| | |_shader|{{RootFieldType|AssetRef`1|[[Type:Shader|Shader]]}}|TypeAdv1=true| | ||
|TextureScale|Float2| | |TextureScale|Float2| How much to scale up or down the scale of the albedo, emissive, normal, height, metallic, and occlusion maps. | ||
|TextureOffset|Float2| | |TextureOffset|Float2| How much to shift around the position of the albedo, emissive, normal, height, metallic, and occlusion maps. | ||
|DetailTextureScale|Float2| | |DetailTextureScale|Float2| How much to scale up or down the scale of the detail albedo, and detail normal maps. | ||
|DetailTextureOffset|Float2| | |DetailTextureOffset|Float2| How much to shift around the position of the detail albedo, and detail normal maps. | ||
|AlbedoColor| | |AlbedoColor|ColorX| The color to multiply the texture of the albedo (base color) with. Basically a tint. Default white. | ||
|AlbedoTexture|ITexture2D| | |AlbedoTexture|{{RootFieldType|AssetRef`1|[[Type:ITexture2D|ITexture2D]]}}|TypeAdv7=true| The texture to use as the color of the surface. | ||
|EmissiveColor| | |EmissiveColor|ColorX| The color to multiply the texture of the emission (glowly color) with. Basically a tint. Default white. | ||
|EmissiveMap|ITexture2D| | |EmissiveMap|{{RootFieldType|AssetRef`1|[[Type:ITexture2D|ITexture2D]]}}|TypeAdv9=true| The texture to use as the glowing (emission) color of the surface. | ||
|NormalScale|Float| | |NormalScale|Float| How much to scale up the effect of the normal map. | ||
|NormalMap|ITexture2D| | |NormalMap|{{RootFieldType|AssetRef`1|[[Type:ITexture2D|ITexture2D]]}}|TypeAdv11=true| The normal map is used as a way to change the appearance of a surface when shined on by lights, to give the illusion of a raised surface. | ||
|HeightMap|ITexture2D| | |HeightMap|{{RootFieldType|AssetRef`1|[[Type:ITexture2D|ITexture2D]]}}|TypeAdv12=true| The height map changes the position that pixels of the surface are rendered so they appear further or closer to the actual surface. Like a parallax effect. Can cause artifacts around edges. | ||
|HeightScale|Float| | |HeightScale|Float| How strong the height parallax effect should be. | ||
|OcclusionMap|ITexture2D| | |OcclusionMap|{{RootFieldType|AssetRef`1|[[Type:ITexture2D|ITexture2D]]}}|TypeAdv14=true| | ||
|DetailAlbedoTexture|ITexture2D| | |DetailAlbedoTexture|{{RootFieldType|AssetRef`1|[[Type:ITexture2D|ITexture2D]]}}|TypeAdv15=true| A multiplied layer of albedo on top of the default <code>AlbedoTexture</code>. | ||
|DetailNormalMap|ITexture2D| | |DetailNormalMap|{{RootFieldType|AssetRef`1|[[Type:ITexture2D|ITexture2D]]}}|TypeAdv16=true| A layered normal map on top of the default <code>NormalMap</code>. | ||
|DetailNormalScale|Float| | |DetailNormalScale|Float| How much to scale up the effect of the detail normal map. | ||
|BlendMode|BlendMode| | |BlendMode|BlendMode|{{Template:Material_BlendMode_Desc}} | ||
|AlphaCutoff|Float| | |AlphaCutoff|Float| If <code>BlendMode</code> is set to cutout, discard rendering of pixels for the surface that fall below this alpha threshold. | ||
|OffsetFactor|Float| | |OffsetFactor|Float|{{Template:Material_OffsetFactor_Desc}} | ||
|OffsetUnits|Float| | |OffsetUnits|Float|{{Template:Material_OffsetUnits_Desc}} | ||
|RenderQueue|Int| | |RenderQueue|Int|{{Template:Material_RenderQueue_Desc}} | ||
|Metallic|Float| | |Metallic|Float| How much metallicness the surface should have if <code>MetallicMap</code> is not specified. | ||
|Smoothness|Float| | |Smoothness|Float| How much smoothness the surface should have if <code>MetallicMap</code> is not specified. | ||
|MetallicMap|ITexture2D| | |MetallicMap|{{RootFieldType|AssetRef`1|[[Type:ITexture2D|ITexture2D]]}}|TypeAdv25=true| [[#Metallic Maps]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 93: | Line 93: | ||
</translate> | </translate> | ||
[[Category:Components{{#translation:}}| | [[Category:Components{{#translation:}}|PBS Metallic]] | ||
[[Category:Components:Assets:Materials{{#translation:}}| | [[Category:Components:Assets:Materials{{#translation:}}|PBS Metallic]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Materials{{#translation:}}|PBS Metallic]] | ||
[[Category:ComponentStubs]] | |||
Revision as of 00:50, 14 November 2024
This article or section is a Stub. You can help the Resonite Wiki by expanding it.
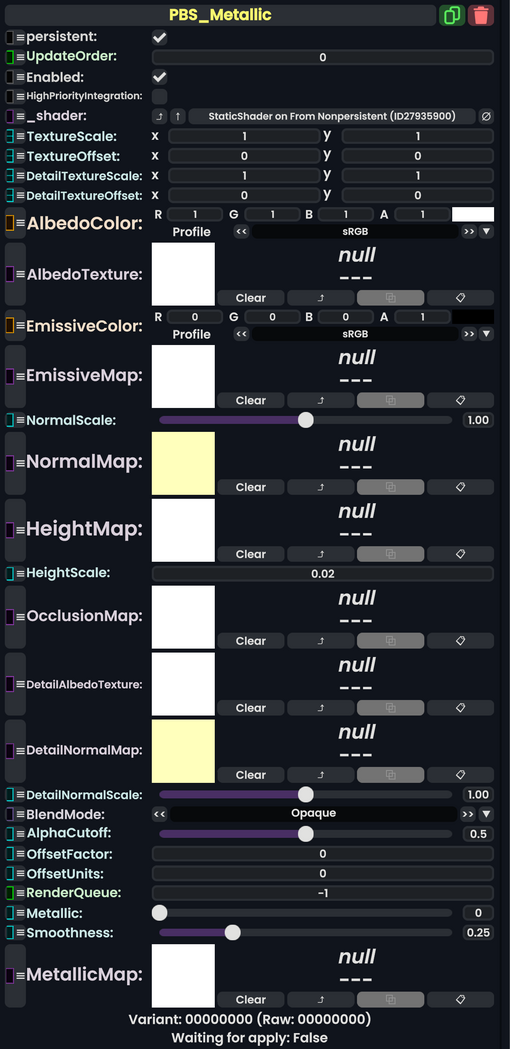
PBS Metallic is a physically-based material that uses a Metallic-Smoothness (MS) map to store data about the metallicity and smoothness of an object. It is based on the Unity 5 Standard PBR Setup.
For information about the maps and their properties read on!
Usage
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
persistent
|
Bool | Determines whether or not this item will be saved to the server. |
UpdateOrder
|
Int | Controls the order in which this component is updated. |
Enabled
|
Bool | Controls whether or not this component is enabled. Some components stop their functionality when this field is disabled, but some don't. |
HighPriorityIntegration
|
Bool | If true, integrating this asset (e.g. processing procedural assets) gets higher priority than assets with this flag off. An example is user laser procedural meshes. |
_shader
|
Shader | |
TextureScale
|
Float2 | How much to scale up or down the scale of the albedo, emissive, normal, height, metallic, and occlusion maps. |
TextureOffset
|
Float2 | How much to shift around the position of the albedo, emissive, normal, height, metallic, and occlusion maps. |
DetailTextureScale
|
Float2 | How much to scale up or down the scale of the detail albedo, and detail normal maps. |
DetailTextureOffset
|
Float2 | How much to shift around the position of the detail albedo, and detail normal maps. |
AlbedoColor
|
ColorX | The color to multiply the texture of the albedo (base color) with. Basically a tint. Default white. |
AlbedoTexture
|
ITexture2D | The texture to use as the color of the surface. |
EmissiveColor
|
ColorX | The color to multiply the texture of the emission (glowly color) with. Basically a tint. Default white. |
EmissiveMap
|
ITexture2D | The texture to use as the glowing (emission) color of the surface. |
NormalScale
|
Float | How much to scale up the effect of the normal map. |
NormalMap
|
ITexture2D | The normal map is used as a way to change the appearance of a surface when shined on by lights, to give the illusion of a raised surface. |
HeightMap
|
ITexture2D | The height map changes the position that pixels of the surface are rendered so they appear further or closer to the actual surface. Like a parallax effect. Can cause artifacts around edges. |
HeightScale
|
Float | How strong the height parallax effect should be. |
OcclusionMap
|
ITexture2D | |
DetailAlbedoTexture
|
ITexture2D | A multiplied layer of albedo on top of the default AlbedoTexture.
|
DetailNormalMap
|
ITexture2D | A layered normal map on top of the default NormalMap.
|
DetailNormalScale
|
Float | How much to scale up the effect of the detail normal map. |
BlendMode
|
BlendMode | How to blend this material's colors vs what it rendered on top of. |
AlphaCutoff
|
Float | If BlendMode is set to cutout, discard rendering of pixels for the surface that fall below this alpha threshold.
|
OffsetFactor
|
Float | how much this material should be pushed forwards or backwards on the depth buffer factor wise |
OffsetUnits
|
Float | how much this material should be pushed forwards or backwards on the depth buffer unit wise |
RenderQueue
|
Int | changes at which point a material renders on the render stack |
Metallic
|
Float | How much metallicness the surface should have if MetallicMap is not specified.
|
Smoothness
|
Float | How much smoothness the surface should have if MetallicMap is not specified.
|
MetallicMap
|
ITexture2D | #Metallic Maps |
Behavior
Metallic Maps
This Material type uses a Metallic Map for determining:
- Metallic Levels
- Ambient Occlusion/Height
- Smoothness
This information is packed into different channels within the Metallic Map using the following pattern:
- R(Red Channel): Metallic
- The Red Channel determines how metallic a material is.
- Metals are usually 1 in this channel and non-metals (also known as dielectrics) are 0
- When choosing Metallic values, do remember that items in the real world aren't perfect. Imperfections and randomness is good! A common misconception is that pixels within a metallic map must be pure 0 or 1 values, however this is not the case. If you were able to zoom in far enough into a material you could observe pure metal and pure non-metal parts (rust would be metal with a separate layer of oxidized material), but with textures, you only have a limited number of pixels to represent individual characteristics of materials. When authoring these textures, what you are actually doing is describing the average characteristic in the area of interest. It is therefore accurate to describe materials such as rust as somewhere between 0 and 1 on average in an area depending on how much oxidation versus metal there is.
- G (Green Channel): Ambient Occlusion/Height
- This allows you to pack either the Ambient Occlusion or the Height map data into one image and re-use it in those inputs to the material, depending on which you prefer to use.
- Alpha: Smoothness
- High Alpha means High Smoothness
- Low Alpha is Low Smoothness
Resonite uses the Unity Standard Shader Maps for this Material, for more information please see this guide for more information.
Other Maps
TODO
Unity declares Green : Occlusion and Height as interchangeable and usable for both slots
https://forum.unity.com/threads/standard-shader-metallic-texture-packing.314283/
R: Metalness
G: Occlusion/Height
A: Smoothness
Examples
Further Reading
You may be interested in the following other pages:
- PBS Specular - Documentation on Resonite's PBS Specular Material. This is often paired or compared to PBS Metallic.