Created page with "Voir aussi: Slot (Type)" |
Created page with "Chaque objet dans Resonite est un '''Slot'''. Les slots forment des ''hiérarchies'', existent dans un espace 3D via des ''transformations'' et contiennent des ''Composants'' qui ajoutent des comportements." |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<languages/> | <languages/> | ||
Chaque objet dans Resonite est un '''Slot'''. Les slots forment des ''hiérarchies'', existent dans un espace 3D via des ''transformations'' et contiennent des ''[[Component|Composants]]'' qui ajoutent des comportements. | |||
== Propriétés basiques == | |||
=== Hiérarchie === | |||
< | [[File:Example_Slot_Hierarchy.webp|thumb|300px|Une hiérarchie simple, montrée dans un [[Scene Inspector|Inspecteur de Scènes]].|alt=<span lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr">A hierarchy of slots as shown in the Scene Inspector. The Example slot has three children, the first of which has another child itself.</span>]] | ||
< | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
A slot can contain zero or more slots, forming a '''hierarchy''' or "'''tree'''". A slot is a '''child''' if it is contained within another slot; that slot is its '''parent'''. The only slot without a parent is the '''root''' of the world, which contains all other slots. | |||
</div> | |||
<span lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr">This hierarchy is used for organization, transformation (see below), and many other features in [[Resonite]].</span> | |||
=== <span lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr">Transformation</span> === | |||
<span lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr">Every slot can be '''transformed''' in 3D space: it can be translated (moved), rotated, and scaled. A child slot's transformation is relative to its parent, so even though a child slot might specify no transformation, in global space it may be rotated or scaled because its parents are. Thus, a child's transform is called "local".</span> | |||
=== <span lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr">Components</span> === | |||
<span lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr">''Main article: [[Component|Component]]''</span> | |||
<span lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr">Slots contain '''components''', which provide almost all the functionality in Resonite. See the main article for details.</span> | |||
=== <span lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr">Fields</span> === | |||
<span lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr">Similar to [[Component]]s, slots have a number of fields that can be modified:</span> | |||
{{Table TypeFields | |||
|Name|String|<span lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr">The name of the component, as shown in the scene inspector.</span> | |||
|Parent|Slot|<span lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr">A reference to the parent slot in the hierarchy.</span> | |||
|Tag|String|<span lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr">A string tag used for identifying slots in various systems.</span> | |||
|Active|Bool|<span lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr">A general-purpose field to "disable" this slot and its components. If a slot is deactivated, its children are deactivated too. Note that not all components and features respect this field.</span> | |||
|Persistent|Bool|<span lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr">Whether this slot will be saved, for example to the [[Inventory]]. If this is disabled, the slot and all its descendants will not be saved.</span> | |||
|Position|Float3|<span lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr">The position offset this slot has relative to its parent.</span> | |||
|Rotation|FloatQ|<span lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr">The rotation this slot has relative to its parent.</span> | |||
|Scale|Float3|<span lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr">The scale this slot has relative to its parent.</span> | |||
|OrderOffset|Long|<span lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr">Controls the sort order of this control relative to its siblings. Slots with a higher value are "after" sibling with a lower value. This controls the order both in the scene inspector, and in many of Resonite's internal processes.</span> | |||
}} | |||
== <span lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr">Working With Slots</span> == | |||
=== <span lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr">With the Scene Inspector</span> === | |||
<span lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr">As a user, slots are primarily manipulated through the [[Scene Inspector|Scene Inspector]]. You can view, create, destroy and modify slots and their components.</span> | |||
=== <span lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr">With ProtoFlux</span> === | |||
<span lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr">[[ProtoFlux]] has a set of nodes for working with the slot hierarchy, see [[:Category:ProtoFlux:Slots]] for a list. Note that access to a slot's components is currently limited.<ref>{{CiteResoniteIssue|57|A way to use components on Protoflux}}</ref></span> | |||
== <span lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr">References</span> == | |||
Revision as of 08:35, 6 March 2024
Chaque objet dans Resonite est un Slot. Les slots forment des hiérarchies, existent dans un espace 3D via des transformations et contiennent des Composants qui ajoutent des comportements.
Propriétés basiques
Hiérarchie
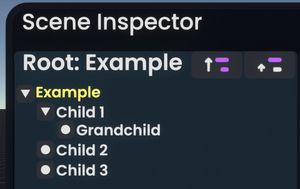
A slot can contain zero or more slots, forming a hierarchy or "tree". A slot is a child if it is contained within another slot; that slot is its parent. The only slot without a parent is the root of the world, which contains all other slots.
This hierarchy is used for organization, transformation (see below), and many other features in Resonite.
Transformation
Every slot can be transformed in 3D space: it can be translated (moved), rotated, and scaled. A child slot's transformation is relative to its parent, so even though a child slot might specify no transformation, in global space it may be rotated or scaled because its parents are. Thus, a child's transform is called "local".
Components
Main article: Component
Slots contain components, which provide almost all the functionality in Resonite. See the main article for details.
Fields
Similar to Components, slots have a number of fields that can be modified:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Name
|
String | Parent |
Slot
|
Tag | String |
Active
|
Bool | Persistent |
Bool
|
Position | Float3 |
Rotation
|
FloatQ | Scale |
Float3
|
OrderOffset | Long |
Working With Slots
With the Scene Inspector
As a user, slots are primarily manipulated through the Scene Inspector. You can view, create, destroy and modify slots and their components.
With ProtoFlux
ProtoFlux has a set of nodes for working with the slot hierarchy, see Category:ProtoFlux:Slots for a list. Note that access to a slot's components is currently limited.[1]